Understanding Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Symptoms, Treatment, and Complications
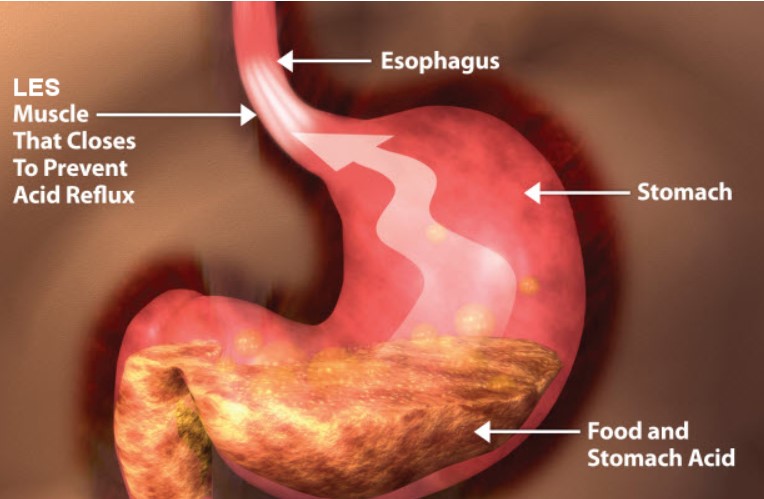
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) affects approximately 20 percent of people in the United States, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Acid reflux is the main symptom of GERD and can cause an uncomfortable burning sensation in the chest, known as heartburn. GERD can cause other symptoms, such as nausea, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, and a hoarse voice. If you experience symptoms of acid reflux more than twice a week, you may have GERD, which can cause serious complications if left untreated.
Your doctor may suggest lifestyle changes to manage GERD symptoms, including maintaining a moderate weight, quitting smoking, avoiding large meals in the evening, waiting several hours after eating before lying down, and elevating your head during sleep. Over-the-counter (OTC) medications like antacids and H2 receptor blockers can also help manage GERD symptoms. It is important to note that while H2 blockers are typically available OTC, one type of H2 blocker (ranitidine or Zantac) was recently recalled by the FDA due to containing the known carcinogen N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA).
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can be prescribed to help manage GERD symptoms. PPIs tend to work better than H2 blockers and can be more helpful in healing the esophageal lining, which can become damaged with long-term GERD. It is important to talk with your doctor before starting any new treatments. While home remedies may help ease occasional bouts of acid reflux, they may not be effective for GERD, which is typically a chronic issue. If you suspect you may have GERD, it is best to talk with your doctor before starting any new treatments.
Some home remedies for acid reflux may do more harm than good, such as drinking a baking soda and water solution, consuming ginger, or drinking milk. If your doctor suspects you may have GERD, they will conduct a physical exam and ask about any symptoms you have been experiencing. Your doctor may recommend you to a gastroenterologist or conduct certain tests, such as an ambulatory 24-hour pH probe, esophogram, or upper endoscopy.
GERD can cause serious complications if left untreated, such as esophagitis, esophageal stricture, Barrett’s esophagus, and esophageal cancer. If you have GERD, it is important to work with your doctor to manage your symptoms and reduce your risk of complications. With proper management, most people with GERD can find relief from their symptoms.
In a recent interview, Dr. Johnson, a gastroenterologist, shared his thoughts on GERD and its management. He stressed the importance of working with a doctor to develop a personalized treatment plan. “GERD is a chronic condition, and it’s important to have a long-term plan for managing it,” he said. “This may include lifestyle changes, medication, or a combination of both. It’s important to work with your doctor to find the right approach for you.”
Dr. Johnson also emphasized the importance of early detection and treatment for GERD. “If left untreated, GERD can cause serious complications,” he said. “It’s important to talk with your doctor if you are experiencing symptoms of acid reflux more than twice a week.”
In addition to lifestyle changes and medication, there are other steps you can take to manage GERD symptoms. For example, avoiding trigger foods and drinks like chocolate, coffee, alcohol, and fatty or fried foods can help reduce symptoms. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can also help.


