Cholesterol is a type of fat that is found in the blood and is essential for the body to function properly. However, too much cholesterol can build up in the arteries and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. There are two types of cholesterol: high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL). HDL is often referred to as the “good” cholesterol, while LDL is referred to as the “bad” cholesterol. In this article, we will discuss lifestyle changes that can help lower LDL cholesterol levels.
Understanding Bad Cholesterol: Cholesterol is a waxy substance that is produced in the liver and is also found in certain foods. LDL cholesterol is considered the “bad” cholesterol because it can build up in the arteries and form plaque, which can narrow the arteries and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
High LDL cholesterol levels can be caused by several factors, including a diet high in saturated and trans fats, being overweight or obese, lack of physical activity, smoking, and genetics. In some cases, high LDL cholesterol levels may also be caused by underlying medical conditions such as hypothyroidism or diabetes.
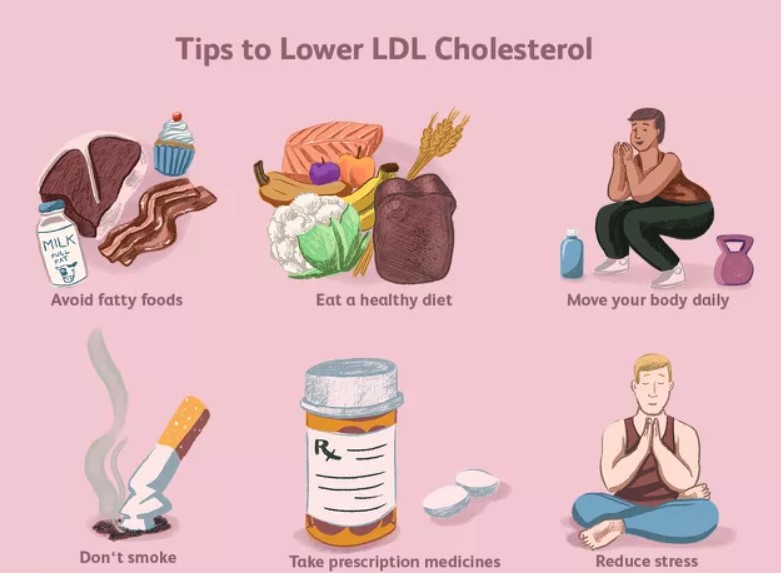
Dietary Changes to Lower Bad Cholesterol: One of the most effective ways to lower LDL cholesterol levels is to make dietary changes. A heart-healthy diet is one that is low in saturated and trans fats and high in fiber, lean protein, and healthy fats.
- Avoid Saturated and Trans Fats: Saturated fats are found in foods such as fatty meats, butter, cheese, and cream. Trans fats are found in processed foods such as baked goods, snack foods, and fried foods. These fats can raise LDL cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease. Instead, opt for healthier fats such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in foods such as nuts, seeds, avocado, and fatty fish.
- Eat More Fiber: Fiber is found in foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Eating a diet high in fiber can help lower LDL cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol and removing it from the body.
- Include Lean Proteins: Choose lean proteins such as fish, skinless poultry, and legumes instead of fatty meats. These proteins are low in saturated fat and high in protein, making them a healthier choice.
Exercise and Physical Activity: Regular physical activity can help improve cholesterol levels by increasing HDL cholesterol levels and lowering LDL cholesterol levels. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Exercise can also help with weight loss, which can lower LDL cholesterol levels. Being overweight or obese can raise LDL cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
Quit Smoking: Smoking can damage the walls of the blood vessels, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup. Quitting smoking can improve cholesterol levels and overall health.
Limit Alcohol Intake: Drinking too much alcohol can raise LDL cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease. The American Heart Association recommends limiting alcohol intake to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
Medications: In some cases, lifestyle changes may not be enough to lower LDL cholesterol levels. Your doctor may prescribe medications such as statins or cholesterol absorption inhibitors to help manage your cholesterol levels. It’s important to take medications as prescribed and to work with your doctor to monitor your cholesterol levels and overall health.


